Patents can provide insights regarding technical details for the smartphone payment transaction process such as Apple Pay, Samsung Pay and Android Pay. Followings illustrate the technical details for each step of the smartphone payment transaction process based on the related patents’ disclosures.
Step 1 The first step in the mobile payment transaction process is to initiate the wireless communication link between customer’s smartphone and Point of Sale (POS) terminal at a shop.
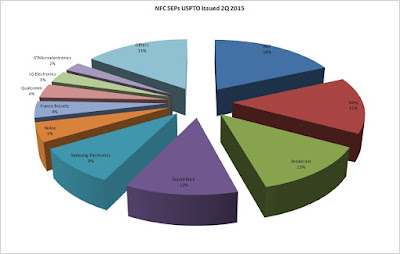
US8838023 (Method and device for active load modulation by inductive coupling; Inside Secure) illustrates the inductive coupling communication techniques adopted in the Near Field Communication (NFC) technology. The standard of NFC (e.g., ISO/IEC18092) defines two communication modes, an active mode (transmitting party) and a passive mode (receiving party). The transmitting and receiving devices are equipped with an antenna coil. The active device emits a magnetic field oscillating, for example, at 13.56 MHz, and sends data to the passive device by modulating the magnetic field: either modifying the impedance of the antenna coil of the passive device at the rate of a data-carrying load modulation signal (passive load modulation) or transmitting bursts of alternating magnetic field at the rate of the data carrying modulation signal (active load modulation). The magnetic field bursts are perceived by the active device as a passive load modulation. Integrate NFC functionality in Smartphones requires small loop antennas, and thus, active load modulation is usually used.


US8813182 (Near field communication activation and authorization; PayPal) illustrates a method of activation and authorization of a NFC enabled device. The payment application activation may begin with the user entering login information, and then, forwards the information and a public key (unique identifier). In response to receiving the user's information and unique identifier, the service provider system sends packet information to the mobile device. The packet information from the payment provider system to the mobile device may include data relating to activation code and/or security keys. A corresponding code generated by the application is then communicated back to the payment provider system from the mobile device. In this regard, such a back-and-forth communication or “handshake” between the mobile device and the payment provider system allows for user and/or system verification, authorization, and compatibility check to complete the application activation process.
US8626066 (Near field communication device; NXP) illustrates a system to switch between passive mode and active mode. A control unit is adapted for switching the communication unit from the passive operating state to the active operating state upon receipt of a configuration signal received from the external device. The control unit is also adapted for controlling the communication unit to the active operating state by exposing the card emulation feature using only the card emulation parameters for RF initialization.
In case that the POS terminal does not have the NFC capability, the magnetic stripe transmission (MST) technique can be used as in Samsung Pay. Magnetic stripe payment cards carry a magnetic stripe that contains the payment card data. Magnetic stripe payment cards include credit, debit, gift, and coupon cards, among others. The data is "written" onto the magnetic stripe by alternating the orientation of the magnetic particles embedded into the stripe. Card data is read from the magnetic stripe at a POS by swiping the card through a magnetic stripe reader. The reader includes of a reader head and its associated decoding circuitry. When the card is swiped through the reader the magnetic stripe moves in front of the reader head. The moving magnetic stripe, which contains the alternating polarity magnetic domains, creates a fluctuating magnetic field within the narrow sensing aperture of the reader head. The reader head converts this fluctuating magnetic field into an equivalent electrical signal. The decoding circuitry amplifies and digitizes this electrical signal, recreating the same data stream that was originally written onto the magnetic stripe. The encoding of the magnetic stripe is described in the international standard ISO 7811 and 7813. As illustrated in US20150235204 (System and method for a baseband nearfield magnetic stripe data transmitter; Looppay), the magnetic stripe transmission (MST) technique enables the transmission of the magnetic stripe data at baseband.
The MST device includes a driver and an inductor, and the MST device is configured to receive the stream of pulses from the mobile phone, to amplify and shape the received stream of pulses and to generate and emit high energy magnetic pulses including the magnetic stripe data of the payment card. The inductor is driven by a series of timed current pulses that result in a series of high energy magnetic pulses that resemble the fluctuating magnetic field created by a moving magnetic stripe.
Step 2 The second step in the mobile payment transaction process is to send the credit/bank card information from the smartphone to the POS terminal. The payment button in the smartphone is programmed to be associated with a pre-selected payment card and activating of the payment button initiates the transfer of card information data of the pre-selected payment card.
The NFC mobile payment enable smartphone includes the secure element (SE) that is coupled to an NFC controller The SE is typically a tamper-resistant piece of hardware (e.g., an integrated circuit) with secure memory that enables the implementation of security-sensitive applications. The credit/bank card information is encrypted and stored in the SE. The embedded software (e.g., applet) inside the SE emulates credit/bank card. The NFC controller interfaces the SE and the NFC RF communication unit to encode/modulate and send the data that includes the credit/bank card information processed in the SE.
US8761664 (Near field connection establishment; Nokia) illustrates the operation of the NFC controller to interface the SE and the NFC RF communication unit. The NFC controller is configured to activate, via the switch, establishment of a NFC connection through the RF communication unit to the SE in response to the RF communication unit detecting an external radio frequency field for establishment of a NFC connection by an external device; and identify a NFC connection attempt addressed to a functionality of the hosting device instead of a NFC connection attempt addressed to a functionality of the SE from the external device.
US8706081 (Packet inspection in near field communication controller for secure element protection; Google) illustrates a method for packet inspection in a NFC controller for SE protection. The functionality of the SE can be implemented by the applets. An applet can refer to an application, program, or other type of software that is used to perform a particular task. Because the platform of a secure element is typically closed, users do not generally have privileges to install and/or update applets on their own. Instead, such tasks are handled by third-party service providers known as Trusted Service Managers (TSMs). Moreover, the applets provided to a SE are often subject to a certification requirement. For example, when a communication device is being used as an electronic wallet, a financial services or payment processing entity may need to approve any applet installation and/or update. As a result, when a security vulnerability is discovered in connection with an applet, the delivery of an approved applet update through the proper third-party service provider can take a significant amount of time. Until the code update is received and installed, the SE remains exposed to the security flaw. The NFC controller can have a memory containing executable instructions that cause the NFC controller to perform a method for handling data. The method performed by the NFC controller includes receiving one or more filtering rules corresponding to security (e.g., a security fix) for an applet in the SE, receiving a data packet for the SE, and determining whether to communicate the data packet to the SE based on the one or more filtering rules.
US8380977 (Peer-to-peer communication method for near field communication; Samsung) illustrates a peer-to-peer communication method for NFC to provide the required link-level security to an NFC terminal during peer-to-peer communication. A link-level security is started by exchanging a link-level security request and a link-level security response between an initiator terminal and a target terminal. Transmission data are encrypted at link-level security layers of the initiator terminal and the target terminal, and the encrypted data are exchanged between the initiator terminal and the target terminal. The link-level security is released by exchanging a link-level security release request and a link-level security release response between the initiator terminal and the target terminal.
Step 3 The final step in the mobile payment transaction process is to send the credit/bank card information and purchase information from the POS terminal to the acquirer, and then, to the issuer to authorize the payment transaction. An authorization code is sent to the acquirer if there is valid credit available. The acquirer authorizes the payment transaction, and then, the customer finalizes the payment through authorization/ authentication.

US8566239 (Mobile commerce systems and methods; First Data Corporation) illustrates a method for utilizing mobile electronic devices in various types of financial transactions. Merchants and service providers accept many forms of payment. Many merchants will accept cash, credit cards, debit cards, stored-value cards, checks, and promotional items such as coupons. All of these forms of payment are often carried by a consumer because some merchants and/or service providers may only accept some of the various possible forms of payment. Sometimes, a customer may not pre-plan a visit to a specific merchant and/or service provider. So, the consumer may wish to carry the different forms of payment in case the consumer does happen to make an unplanned visit. The method of providing a plurality of mobile commerce functions comprises receiving a communication related to a function of a mobile wallet application of a mobile device. Acquirer systems for handling of the communication can be identified based on the function of the mobile wallet application to which the communication relates. The communication can be routed to the identified acquirer systems for handling of the communication. In some cases, a reply to the communication can be received from the identified acquirer systems and the reply can be sent to a recipient.
US8090657 (Method and apparatus for authenticating financial transactions; Electronic Finger Print Technologies) illustrates a system for authentication of financial transactions using a mobile terminal includes apparatus for sampling a unique biological identifier of a system user. The user may complete a transaction by using a unique biological identifier in place of the credit card without requiring either the customer's signature or the entry of a PIN. The unique biological identifier is preferably a finger print.
©2015
TechIPm, LLC All Rights Reserved http://www.techipm.com/